Change Virtual Memory Settings to speed up Windows
Virtual memory for your computer is hard drive space used by Windows when it fills up the physical RAM.
When your system runs low on RAM because an application like Firefox is taking too much memory, Windows moves the least used "pages" of memory out to a hidden file named pagefile.sys in the root of one of your drives to free up more RAM for the applications you are actually using. What this actually means to you is that if you've had an application minimized for a while, and you are heavily using other applications, Windows is going to move some of the memory from the minimized application to the pagefile since it's not being accessed recently. This can often cause restoring that application to take a little longer, and your hard drive may grind for a bit.
If you want to take a look at your own pagefile settings, launch sysdm.cpl from the Start menu search or run box (Win+R) and navigate to Advanced –> Settings –> Advanced –> Change.
By default, Windows uses the boot partition (the partition that contains your operating system files) and it is recommended to set the size of the paging file to 1.5 times the amount of RAM that you have.
To change the virtual memory settings, go to "Start", "Control Panel" and click on "System". Click on the "Advanced tab" and under the "Performance" box, click "Settings". In Windows 7, you’ll need to click on "Advanced System Settings" on the left side to bring up the "System Properties" dialog.
On the "Performance" dialog, click the "Advanced" tab and then click "Change" under the "Virtual Memory" heading.
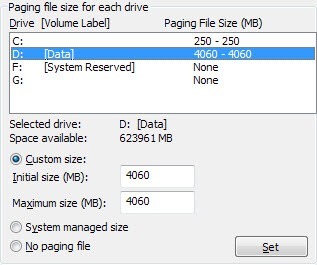
Now you’ll see the Virtual Memory settings as shown below. In Windows 7 and higher, the "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives" box is checked by default.
To get the best performance it is best to create a paging file on a different partition than the boot partition (the drive that contains that operating system, which is usually the C drive) and to also create it on a separate hard drive. In this way, Windows can handle more I/O requests because the paging file will not have to compete with the system folder that needs to be constantly accessed as Windows runs.
Set the initial and maximum sizes for paging file to the same number to reduce fragmentation of the paging file.
Create paging file on the boot partition and set the initial and maximum sizes to 1.5 times the amount of RAM you have.
Windows services which are safe to disable?
- Print Spooler - if you don’t use a printer or print-to-PDF
- Remote Registry - it’s not usually running by default, but you can disable it for safety